RFID is the abbreviation of RadioFrequencyIdenTIficaTIon, which is radio frequency identification, which is a non-contact automatic identification technology. It automatically recognizes the target object and acquires relevant data through the RF signal, and the identification work can work in various harsh environments without manual intervention. RFID technology can recognize high-speed moving objects and recognize multiple labels at the same time, which is quick and easy to operate. For example, when the RFID tag enters the magnetic field, it receives the RF signal from the reader, and sends the product information (Passive Tag, Passive Tag or Passive Tag) stored in the chip by the energy obtained by the induced current, or actively sends a certain one. Frequency signal (AcTIve Tag, active tag or active tag); the reader reads the information and decodes it, and sends it to the central information system for data processing. RFID technology is now widely used on non-contact IC cards, such as contactless cards with a carrier frequency of 13.56 MHz and a read/write distance of less than 10 cm. In response to the needs of industry application development, Guangzhou Unicom has superimposed CPU, memory, NFC chip and RF antenna on the WCDMA-USIM card to enable RFID technology to be applied to mobile phones, bringing new feelings to mobile phone users. . At present, there are many sets of systems closely related to card, card, ticket and cash use in the university area, such as: supermarket consumption system, library management system, dormitory access control system, computer room management system, school bus system, hot water supply system, etc. Because each system has a corresponding independent management system, it brings certain inconvenience to the unified management, financial management and student use of the school. Guangzhou Unicom proposed to build a mobile phone card platform based on 2.4GHZRF-USIM card technology, integrating all the systems in the school that are closely related to cards, certificates, tickets and cash usage, and replacing one with a mobile phone. Cards, certificates, tickets, and cash, thus facilitating the teaching, research, study, life and management of the school's teachers and students. While facilitating the majority of teachers and students, improve the management level and service level of the school, reduce the investment of schools, teachers and students in cards, certificates and tickets, and also achieve financial in the process of replacing the original cards, certificates, tickets and cash. The purpose of the management. The mobile phone card platform is a mobile phone card system designed by mobile phone mobile payment method. The platform is compatible with RFSIM, SIMPASS, CPU card and MifareOne card mobile phone wallet consumption and payment, and can be fully compatible with various consumer terminal carriers. In addition, the platform adopts the latest 2.4G radio frequency technology and is integrated into the USIM card of the mobile phone, so that the mobile phone user only needs to replace one Unicom intelligent USIM card, so that the existing mobile phone can be turned into an NFC-like mobile phone, which greatly reduces the user. The threshold of use. Not only does it have all the communication features of a regular USIM card, but it also has a full-service platform that can replace wallets, keys and ID cards. Holding such NFC mobile phones can be easily applied to student attendance, campus consumption, dormitory access, library borrowing, parking fees and other card systems. When developing and designing a mobile phone card platform, the USIM is used to replace the commonly used non-contact IC card, and 3G-WCDMA technology can be applied at the same time, and the mobile phone card system in different areas can be connected as a whole at high speed, safely and stably. Meet the requirements of unified management. The mobile phone card platform can bind the USIM smart card number and the IMEI number of the mobile phone and the student's personal information (including portrait photos) in the background, so as to realize the real name system of the mobile phone card. By promoting the mobile phone card business, Unicom's mobile phone business can be infiltrated into every circulation of the school, greatly enhancing the pasteability of students on the mobile phone business, and has important strategic significance for the development of mobile services. Figure 1: Schematic diagram of mobile phone card business The mobile phone card platform consists of the following parts 1. Information exchange system Carding Center: It realizes centralized management of the school's mobile phone card, which is convenient for students and reduces costs. Through the application integration platform, card information can be provided for other application systems integrated into the mobile phone card system to ensure that various application systems have cards available. In order to replace the original card, ticket, and card. Settlement Center: Achieve unified settlement of various consumption and charging records using the mobile phone card to achieve the purpose of financial management. Running the configuration system: It can meet the requirements of the school to customize the mobile phone card system into a personalized system, so that it can better meet the individual management requirements of the college. All applications of the mobile phone card are deployed around the information exchange system (including the information exchange system and application gateway in the figure). The card center system provides card information to other systems through the information exchange system, so as to use the same card to replace the cards, tickets, certificates, and even cash in the original systems. The other systems collect the transaction records generated by the card into the settlement center system through the information exchange system, and perform unified clearing and settlement to the merchant according to the liquidation result. Of course, all application systems can also exchange data freely through the information exchange system to realize information exchange and data sharing between various systems. The overall network structure of the mobile phone card fully embodies the design principle of “standard first, unified planning, step-by-step implementationâ€, and adopts advanced technologies such as JAVA, J2EE, XML, WEBSERVICES, and large-scale relational database management system. Standards first, system security, several applications deployed around the mobile card platform, thus forming a complete mobile phone card system solution. The mobile phone card system is a huge system. The success or failure of its construction involves all aspects. In addition to the selection of various related devices, it is mainly reflected in whether the mobile phone card system has a good application integration design. And the ability to integrate existing systems and integrate systems that are deployed in the future according to school needs. If the mobile phone card system does not solve this problem well, then the mobile phone card platform can only be one that is not open, and there is no technological advancement that can't satisfy the school's mobile phone card system. For the consideration of the advanced nature of the mobile phone card system, it is necessary to examine whether it can meet the construction needs of the campus business itself, but also whether it has sufficient scalability and whether it can be smoothly upgraded in the future according to the needs of the school's own information construction. A digital campus solution that guarantees continuity of use while ensuring long-term effectiveness of the school's investment. At present, Guangdong Unicom has signed a strategic cooperation agreement with Guangdong UnionPay to jointly promote the development of RFID radio frequency technology in mobile payment and mobile e-commerce. We believe that in the near future, RFID radio frequency technology will become the most popular mobile phone application technology and will be promoted by various telecom operators. Guangzhou Unicom has also reached an initial cooperation agreement with Shenzhen Golden Membrane Communication Co., Ltd., which is responsible for the construction of the Guangzhou Unicom campus mobile phone card project by Shenzhen Golden Membrane Communication Co., Ltd. The project adopts the advanced RFID radio frequency technology of Shenzhen Golden Membrane Communication Co., Ltd. and the campus mobile phone card platform, which will provide a strong guarantee for Guangzhou Unicom to advance into the Guangzhou University City to develop campus 3G business. It can be seen that mobile RFID technology plays an important role in attracting students to the public, digging deep into the application of the mobile phone industry, and improving customer convenience services.
A Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) connector, also pounced as [scuzzy" connector, is used for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices.
SCSI is the small computer system interface, which is an independent processor standard used for the system level interface between computer and intelligent devices (hard disk, floppy, optical drive, printer, scanner, etc.). It is an intelligent universal interface standard, which has the function of communicating with various types of peripherals. SCSI uses the standard software interface of ASPI (SCSI programming interface) to make the driver communicate with the SCSI adapter installed inside the computer. SCSI interface is widely used in high-speed data transmission technology on minicomputers. SCSI interface has many advantages, such as wide application range, multitask, wide bandwidth, low CPU utilization, and hot plug.
SCSI connectors type and interfaces
Centronics 50-pin connector: The Centronics 50-pin connector was once the most widely used SCSI connector. An external connector only, the Centronics is a SCSI-1 connector that looks the same as the Centronics cable that attaches to a parallel port printer. The Centronics 50-pin cable comes in male and female styles, and gender changers and cable converters are commonly available. Although used on older SCSI devices and external drive enclosures, this interface is no longer heavily used, due to its slow speed and short cable lengths.
SCSI SFF 8482: Also called "4x internal" by some vendors. This is a connector with the same form factor as SATA with the addition of a "bump" to key it specifically for SAS. (SATA drives can be plugged into SAS controllers, but SAS drives will not function with a SATA controller; hence, the necessity for the key bump on the connector.) As the name says, it's meant to be used internally, i.e., inside the computer case.
SCSI SFF 8484: Also called "32-pin" or "MultiLane". This is a high density connector usually intended to plug into the motherboard, controller, or backplane itself. Cables with this connector on one end usually have four individual SFF 8482 connectors on the other. Scsi Connector,Half Pitch Scsi Connectors,Scsi Lead Half Pitch Male,SCSI (SAS) Connectors,Female Scsi Connector,SCSI Connectors I/O Connectors,Manufacturers and Suppliers in China ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.atkconnectors.com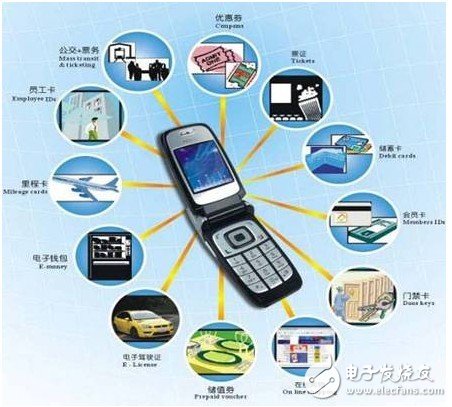
2, universal application gateway
3, card center system
4. Settlement center system
5, running the configuration system
6, monitoring system
7, clearing application server
8. Self-enrollment system The application integration platform (information exchange system and universal application gateway system) of the mobile phone card system: can be used to integrate various existing and future application systems of the college, so that they can communicate with each other and exchange data. To solve the problem of information islands. 
Figure 2: Structure of the mobile phone card system
Network topology diagram: 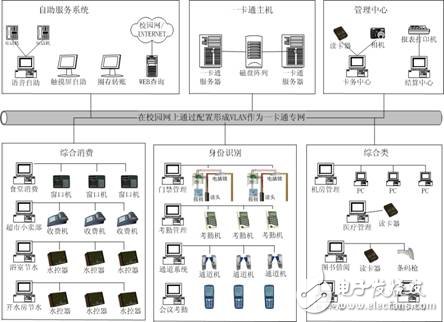
Figure 3: Overall network structure of mobile phone card
High-density 50-pin connector: The high-density 50-pin connector is used on scanners and Jaz drives. It is one of the more common SCSI connectors and is usually used to connect SCSI-2 devices. Both ends of the cable are usually 50-pin male, while the sockets on the host adapter and external devices are 50-pin female.
DB 25-pin connector: The DB 25-pin or D Sub 25 is by far the most widely used connector. This connector is used for parallel and serial printers in addition to the many other devices available. Both ends of the cable are usually 25-pin male, while the sockets on the host adapter and external devices are 25-pin female. This cable is almost always an external connector.
Note: DB-25 SCSI CABLES are not compatible with and should not be used as serial or printer cables; serial cables and printer cables should not be used or attached to DB-25 SCSI adapters. You can short out the SCSI host adapter or the motherboard by using the wrong cable. Marking cables is the best way to avoid this.
IDC50 connector: The IDC50 is the most common internal SCSI connector. It is very similar to the standard IDE internal ribbon cable. The IDC50 SCSI cable is considerably wider then an IDE ribbon cable; in fact, it is usually the widest standard internal cable in use. This is a standard SCSI-2 10MBps internal SCSI cable. Many low-end cables have only two or three connectors, allowing for one or two devices to be attached to the cable. Seven-device cables are available, though they are often expensive and require a large case, as the cables may be four or five feet long.
High-density 68-pin connector: The high-density 68-pin connector is the SCSI connector of choice for SCSI-3 host adapters and peripherals. There is an internal ribbon cable version that looks very similar to the IDC50 connector. Many low-end cables have only two or three connectors, allowing for one or two devices to be attached to the cable. Seven-device cables are available, though they are often very expensive and require a large case, as the cables may be three or more feet long. Both ends of the external cable are usually 68-pin male, while the sockets on the host adapter and external devices are 68-pin female.
SCA 80-pin Micro-Centronics connector: SCA stands for Single Connector Attachment, a type of disk drive connector that includes connection pins for the power cables as well as the data wires. A SCA connector uses an 80-pin plug and socket to connect peripherals. This connector combines power, data channel, and ID configuration for fast installation and removal. SCA connectors are typically found only on high-end SCSI hard disks. The SCA interface was designed to provide a standard connection for systems using drives that can be hot-swapped. SCA makes swapping SCSI hard drives much easier than with traditional SCSI cables, plugs, and sockets. An adapter enables SCA drives to fit into standard SCSI enclosures.
Serial Attached SCSI SFF 8470: Also called "4x external" by some vendors. This is simply a version of the SFF 8484 that's meant to be used with external (i.e., not located within the case) drives.
Overview of RFID RF Technology Applications for Mobile Phones
Foreword